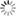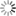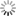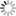
Self-Monitoring A1C and Blood Glucose
- Sep 18, 2023
422 million people worldwide have diabetes according to the World Health Organization.1
A combination of A1C testing and blood glucose monitoring are the main ways to evaluate a person's diabetes treatment plan.2
But what are the differences and why do they matter?
The Goal for most adults with diabetes is to aim to stay below an A1C of 7%4 (NGSP)
|
A1C |
Blood Glucose Monitoring (BGM) |
|
Test 2-4 times/year depending on glycemic control3 |
Tests multiple times a day6 |
|
Provides overall average blood glucose levels over 2-3 months4 |
Measures the state of blood glucose level at any one time; continuously changing7 |
|
Monitors effectiveness of managing or treating diabetes with target A1C goal setting4 |
Used to determine current impact of food, exercise, medication, etc. on the blood glucose8 |
|
Strongly associated with cardiovascular outcomes in patients with diabetes and high cardiovascular risk5 |
Helps identify hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia9 |
BGM can help identify daily impacts on glucose levels; while A1C testing shows the average glucose levels over the last 3 months. Armed with this information from self-monitoring and working closely with their healthcare providers; people living with diabetes can help to ensure they are on the right treatment paths.10
How well is your diabetes treatment plan working?
With the A1CNow® Self Check 4-count system, people with diabetes can…
- Administer quarterly A1C tests at home
- Save time traveling back and forth from in-office visits and lab appointments
- Within minutes, gain clearer understanding of your A1C measurements
System Includes:
- 1 A1CNow Self Check Analyzer
- 4 test cartridges
- 4 lancets
- 4 blood collectors and shakers

Source: MKG 003351